Understanding the Power Behind Electronics: N Channel MOSFET vs P Channel, MOSFET vs Transistor, and How Do MOSFETs Work
In the world of electronic components, the MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) plays a crucial role in the efficiency and control of countless modern devices. Whether you’re designing power management systems, automotive electronics, or consumer devices, understanding the fundamentals and differences between MOSFET types is essential. At Dongguan Tongke Electronic Co., Ltd (brand name: CTK), we are committed to manufacturing high-quality, reliable MOSFETs that support the innovation and reliability our global customers expect.
This comprehensive article explores the key concepts surrounding MOSFETs, especially the differences between N channel and P channel MOSFETs, how they compare to traditional transistors, and the basic principles of how MOSFETs work.
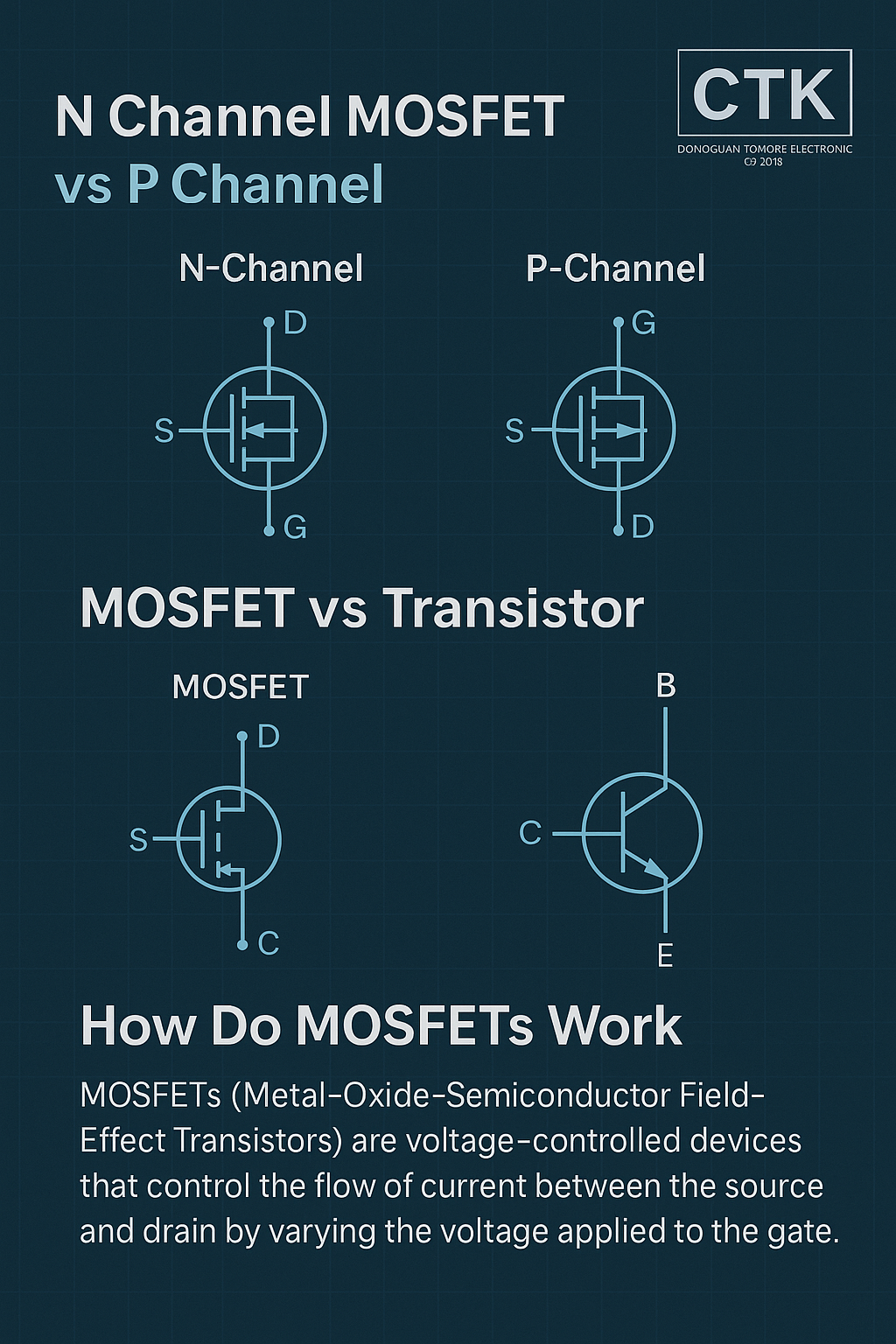
How Do MOSFETs Work?
MOSFETs are a type of field-effect transistor (FET) used for switching and amplifying electronic signals in various devices. Unlike bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), which are current-controlled, MOSFETs are voltage-controlled devices. They work by applying a voltage to the gate terminal, which regulates the current flow between the source and drain terminals.
There are two primary types of MOSFETs:
N Channel MOSFET – where electrons are the charge carriers
P Channel MOSFET – where holes are the charge carriers
The basic working principle is simple:
When a suitable voltage is applied to the gate terminal, it creates an electric field that allows current to flow through the channel (from drain to source in N channel, or source to drain in P channel).
The threshold voltage determines when the MOSFET turns "on" or "off".
MOSFETs are valued for their high efficiency, fast switching speed, and low power loss, making them ideal for applications such as DC-DC converters, motor drivers, and battery management systems.
N Channel MOSFET vs P Channel: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the distinction between N channel and P channel MOSFETs is essential for efficient circuit design:
| Feature | N Channel MOSFET | P Channel MOSFET |
|---|---|---|
| Charge Carrier | Electrons | Holes |
| Conductivity | Higher (lower Rds(on)) | Lower (higher Rds(on)) |
| Switching Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Gate Drive Voltage | Positive relative to source | Negative relative to source |
| Preferred Usage | Low-side switching | High-side switching |
Why N Channel is Often Preferred:
N channel MOSFETs generally offer lower resistance and higher efficiency due to the mobility of electrons being higher than that of holes.
They are ideal for high-current applications and are commonly used in synchronous buck converters, power supplies, and motor control systems.
When to Use P Channel MOSFETs:
P channel MOSFETs are useful when simpler high-side switching is needed, especially in low-current circuits.
They can eliminate the need for a gate driver circuit in certain topologies, making the design process easier.
At CTK, we offer a full range of both N and P channel MOSFETs, allowing designers the flexibility to choose the most appropriate component for their specific needs.
MOSFET vs Transistor: Key Comparisons
While both MOSFETs and traditional bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) are used for switching and amplification, their operational mechanisms differ:
| Feature | MOSFET | BJT |
| Control Type | Voltage-controlled | Current-controlled |
| Input Impedance | High | Moderate |
| Switching Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Power Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Thermal Stability | Better | Lower |
| Drive Power | Low | Higher required |
Why Choose MOSFETs Over BJTs:
MOSFETs offer better efficiency, especially at high switching frequencies.
Their lower gate drive requirements make them more suitable for battery-powered and energy-sensitive applications.
They generate less heat and are more scalable for high-power uses.
However, BJTs may still be preferred in analog circuits where linear amplification is required, while MOSFETs are dominant in switching applications.
Why Choose CTK MOSFETs?
Dongguan Tongke Electronic Co., Ltd (CTK) is a leading manufacturer of MOSFETs, diodes, transistors, TVS, and ESD components. Here’s why global customers trust CTK:
Certified Quality: ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certified factory
15+ Years of Experience in electronic component manufacturing
Comprehensive Product Line: N channel and P channel MOSFETs for various voltage and current ratings
Applications Across Industries: Our products are used in automotive electronics, medical devices, telecom equipment, LED lighting, and more
Trusted by Global Brands: Long-term partners include BYD, TCL, Foxconn, and Skyworth
We support both standard and customized orders, with a strong commitment to fast delivery and technical support.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between N channel and P channel MOSFETs, as well as how MOSFETs compare to BJTs, is essential for selecting the right component for your design. Whether you’re creating a power-efficient mobile device or a robust automotive control unit, CTK’s reliable and efficient MOSFETs provide the performance you need.
For more information or to request a product catalog, feel free to contact our sales team. We’re here to support your success with world-class electronic components.
Contact Us Today and Power Your Innovation with CTK MOSFETs!

Enter your email to hear from us about Product list, Latest Products and Customer application examples!