In the world of electronic components, diodes play a fundamental yet critical role—they are found on virtually every circuit board. Among them, the
1N4007 stands out as a classic rectifier diode, widely adopted due to its high reliability, low cost, and high current capability. This article provides a detailed overview of the key specifications of the 1N4007 (such as reverse voltage, forward current, and recovery time), analyzes its typical application circuits (e.g., bridge rectification and flyback protection), and offers a selection guide comparing it with other models in the 1N400x series.
1. Specification Breakdown
1.1 Electrical Characteristics (Typical @ 25°C)
|
Parameter |
Symbol |
Typical Value |
Test Conditions |
Notes |
|
Forward Voltage Drop |
VF |
1.1 V |
IF = 1 A |
Increases slightly with current |
|
Reverse Leakage Current |
IR |
5 μA |
VR = 1000 V |
Increases at high temperature |
|
Junction Capacitance |
CJ |
15 pF |
VR = 4 V, f = 1 MHz |
Affects high-frequency performance |
|
Thermal Resistance |
RθJA |
50 °C/W |
Without heatsink |
Impacts thermal design |
1.2 Absolute Maximum Ratings
|
Parameter |
Symbol |
Maximum Value |
Description |
|
Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage |
VRRM |
1000 V |
Breakdown may occur if exceeded |
|
Average Forward Current |
IO |
1 A |
Long-term continuous operation limit |
|
Peak Forward Surge Current |
IFSM |
30 A |
8.3 ms single half sine wave pulse |
|
Operating Junction Temperature |
TJ |
-65°C to +175°C |
Beyond range may cause device failure |
1.3 Switching Characteristics
|
Parameter |
Symbol |
Typical Value |
Description |
|
Reverse Recovery Time |
trr |
30 μs |
Affects high-frequency performance |
|
Reverse Recovery Charge |
Qrr |
5 μC |
Major contributor to switching loss |
2. Typical Applications
From the analysis of its core parameters, we can clearly see the limitations and strengths of the 1N4007:
-
1000V reverse voltage makes it ideal for line-frequency rectification
-
1A continuous current suits most low-power applications
-
30 μs recovery time defines its upper frequency limit
2.1 AC Mains Rectification (Core Application)
Use Cases:
-
Household appliances (e.g., fans, chargers, small adapters)
-
Secondary-side rectification of transformers in industrial control systems
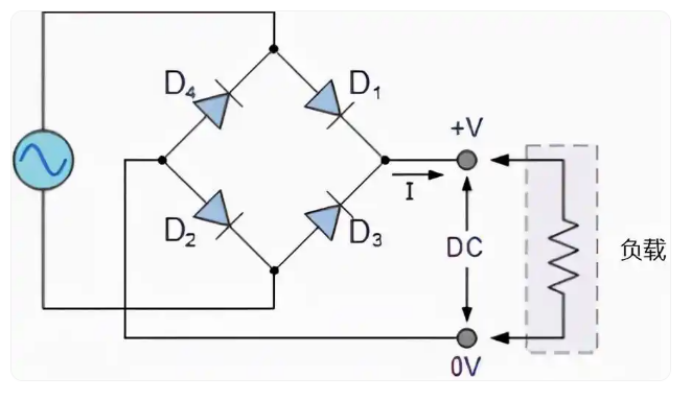
Example: Emergency Fan Power Supply Circuit
The circuit features a bridge rectifier (comprising four 1N4007 diodes), a voltage regulator, and a relay-driven fan switch. The four diodes convert AC to DC, while D1 protects against inductive voltage spikes across the relay coil, and D2 prevents reverse current flow.
Parameter Fit:
-
1000V reverse voltage handles 220V AC input (after transformer step-down, peak voltage is <700V), providing safe margin
-
1A average forward current supports devices in the 5W–20W range such as mobile chargers or LED drivers
Typical Topologies:
-
Full-bridge rectification (4 × 1N4007)
-
Half-wave rectification (1 × 1N4007)
In a full-bridge circuit, the four diodes alternate conduction in each AC half-cycle to deliver a smooth DC output, ensuring stable performance.
2.2 Low-Power DC Protection
Use Cases:
-
As reverse polarity protection diode (series with DC input)
-
As a flyback diode across relays/motors to absorb inductive spikes
Parameter Fit:
-
1A current rating can handle relay or small DC motor pulses
-
High voltage tolerance helps absorb inductive back-EMF (a 12V relay may generate >100V spikes)
2.3 Low-Frequency Pulse Circuits
Use Cases:
-
Low-frequency PWM dimming (e.g., post-TRIAC dimmer for lamps)
-
Low-speed signal detection (e.g., audio peak detection where speed isn't critical)
Limitations:
-
30 μs reverse recovery time restricts operation to frequencies below 1 kHz
-
(Acceptable at 1 kHz; losses increase dramatically above 10 kHz)
3. Selection Guide
In circuit design, the choice of rectifier diode directly affects efficiency, reliability, and cost. As a classic line-frequency rectifier, the 1N4007 is widely used in AC-DC converters, reverse polarity protection, and flyback circuits.
Comparison with 1N400x Series
|
Model |
Max Reverse Voltage |
Avg Rectified Current |
Surge Current |
Typical Applications |
|
1N4001 |
50 V |
1 A |
30 A |
Low-voltage circuits (5V–12V) |
|
1N4002 |
100 V |
1 A |
30 A |
12V–24V power supplies |
|
1N4003 |
200 V |
1 A |
30 A |
24V–48V industrial systems |
|
1N4004 |
400 V |
1 A |
30 A |
Medium-voltage AC (e.g., home appliances) |
|
1N4007 |
1000 V |
1 A |
30 A |
High-voltage rectification (e.g. 220V AC) |
Advantages of 1N4007
High Voltage Tolerance
Capable of directly rectifying 220V AC input. Lower-rated diodes (1N4001–1N4004) may fail under such conditions.
Universal Compatibility
Can replace any lower-rated 1N400x model (e.g., 1N4004) in most cases. However, backward substitution is not safe.
Robustness
Better suited to unstable environments (e.g., industrial power systems with voltage surges).